Aprendizaje experiencial en contextos profesionales militares especializados en aviación
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26423/ag7qne90Palabras clave:
Rango militar, Estilos de aprendizaje, Educación militar, cuestionario KLSIResumen
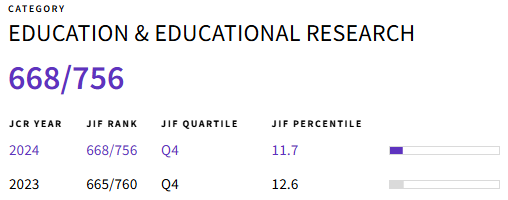
Con base en un diseño no experimental y transversal, se determinaron los estilos de aprendizaje de oficiales de aviación militar ecuatorianos basados en la teoría de Kolb. Se utilizó el cuestionario psicométrico Kolb Learning Style Inventory (KLSI), el cual evalúa cuatro dimensiones: Experiencia-Concreta (EC), Observación-Reflexiva (OR), Conceptualización-Abstracta (CA) y Experimentación-Activa (EA), y contempla cuatro estilos de aprendizaje (Convergente, Divergente, Asimilador y Acomodador). La muestra estuvo compuesta por 97 oficiales activos: Grado 1-Teniente (n=37), Grado 2-Capitán (n=27), Grado 3-Mayor (n=9) y Grado 4-Teniente Coronel (n=24). Se calcularon descriptivos y se desarrolló un Análisis de Varianza (ANOVA). Se identificó un predominio fuerte del estilo Convergente y una orientación que enfatiza la CA y la EA, coherentes con las demandas técnicas y operativas de los oficiales. El resto de los estilos Acomodador (11,34 %), Divergente (10,31 %) y Asimilador (6,19 %), fueron mucho menos frecuentes entre los oficiales de aviación estudiados. No se aprecia diferencias significativas por rangos. La ausencia de estas diferencias sugiere patrones de aprendizaje consistentes a lo largo de la progresión jerárquica en aviación militar. Los estilos descritos sugieren variaciones en las preferencias de aprendizaje, que pueden tener implicaciones prácticas para el diseño curricular educativo, sobre todo a nivel del microcurrículo.
Descargas
Referencias
Abewardhana, A. A. B. D. P.; Seneviratne, G. W. A..; y Kumara, P. P. N. V. (2018). Learning styles of military learners. In Proceedings of the 11th International Research Conference (pp. 46-50). General Sir John Kotelawala Defence University. http://ir.kdu.ac.lk/bitstream/handle/345/2533/Untitled%286%29.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
Bonk, C. J.; y Wisher, R. A. (2000). Applying collaborative and e-learning Tools to Military Distance Learning: A research framework (Technical Report 1107). United States Army Research Institute for the Behavioral and Social Sciences. DOI: https://doi.org/10.21236/ADA393677
Chiang, Cristina.; Wells, Paul. K.; y Xu, Gina. (2021). How does experiential learning encourage active learning in auditing education? Journal of Accounting Education, 54, 100713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaccedu.2020.100713 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaccedu.2020.100713
Cole, R. E.; Rogers, R. L.; Clark, H. L.; y Segrist, L. D. (2013). Incorporation of Learning Styles in the U.S. Military Graduate Program in Nutrition. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 113(9, Supplement), A40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jand.2013.06.133 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jand.2013.06.133
De Jong, David.; y Dexter, Sara. (2025). Experiential learning through simulations in fully online asynchronous courses: Exploring the role of self-debriefing. The Internet and Higher Education, 65, 100976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2024.100976 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2024.100976
Duzhyi, Roman V.; Tetiana Derkach, M. (2024). Learning styles of the Armed Forces of Ukraine personnel undergoing. Educational Technology Quarterly, 2024(1), 97-119. https://doi.org/10.55056/etq.659 DOI: https://doi.org/10.55056/etq.659
Ferrer-Valdivia, N.; Herrera-Barraza, V.; y Garrido-Urrutia, C. (2025). Learning Styles in undergraduate dentistry students: A systematic review. Japanese Dental Science Review, 61, 79-89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdsr.2025.03.004 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdsr.2025.03.004
Fuerzas Armadas del Ecuador. (2021). Modelo Educativo de las Fuerzas Armadas (Abril 2021). https://cetnav.armada.mil.ec/slides/slide/modelo-educativo-de-ffaa-2021-168
Fussell, Stephanie; Dattel, Andrew; y Mullins, Kadie (2018). Personality types and learning styles of collegiate aviation students. International Journal of Aviation, Aeronautics, and Aerospace, 5(3), 1-17. https://doi.org/10.15394/ijaaa.2018.1223 DOI: https://doi.org/10.15394/ijaaa.2018.1223
Gibbs, Mike.; y Priest, Helena. (2010). Exploring the physical health needs of people with learning disabilities: Facilitation student engagement in learning, using Kolb’s experiential learning cycle. Nurse Education in Practice, 10(3), 115-118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nepr.2009.04.005 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nepr.2009.04.005
Healey, M., y Jenkins, A. (2000). Kolb's experiential learning theory and its application in geography in higher education. Journal of Geography, 99(5), 185-195. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221340008978967 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00221340008978967
Hung, Ling-Ya.; Wang, Shun-Mei.; y Yeh, Ting-Kuang Yeh. (2023). Kolb’s experiential learning theory and marine debris education: Effects of different stages on learning. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 191, 114933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.114933 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.114933
Jewett, L. S.; Greenberg, L. W.; Foley, R. P.; Goldberg, R. M., Spiegel, C. T.; y Green, C. (1987). Another look at career choice and learning preferences. Medical Education, 21(3), 244-249. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2923.1987.tb00697.x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2923.1987.tb00697.x
Kirschner, Paul. A. (2017). Stop propagating the learning styles myth. Computers & Education, 106, 166-171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2016.12.006 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2016.12.006
Kolb, A. Y., Kolb, D. A. (2013). The Kolb Learning Style Inventory 4.0: A Comprehensive Guide to the Theory, Psychometrics, Research on Validity and Educational Applications. Experience Based Learning Systems. https://learningfromexperience.com/research-library/the-kolb-learning-style-inventory-4-0/
Kolb, D. A. (1984). Experiential learning experiences as the source of learning development. Prentice Hall.
Kolb, David. A. (2014). Experiential learning: Experience as the source of learning and development. FT press.
Konak, Abdullah.; Clark, Tricia K.; y Nasereddin, Mahdi (2014). Using Kolb’s Experiential Learning Cycle to improve student learning in virtual computer laboratories. Computers & Education, 72, 11-22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2013.10.013 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2013.10.013
Lee, Eric; y Perdana, Arif (2023). Effects of experiential service learning in improving community engagement perception, sustainability awareness, and data analytics competency. Journal of Accounting Education, 62, 100830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaccedu.2023.100830 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaccedu.2023.100830
Li, Ming.; y Armstrong, Steven (2015). The relationship between Kolb’s experiential learning styles and Big Five personality traits in international managers. Personality and Individual Differences, 86, 422-426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2015.07.001 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2015.07.001
Mainemelis, Charalampos; Boyatzis, Richard; y Kolb, David (2002). Learning styles and adaptive flexibility: Testing experiential learning theory. Management Learning, 33(1), 5-33. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1350507602331001 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1350507602331001
Mavin, T. J., & Roth, W.-M. (2015). Optimizing a workplace learning pattern: A case study from aviation. The Journal of Workplace Learning, 27(2), 112-127. https://doi.org/10.1108/JWL-07-2014-0055 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/JWL-07-2014-0055
Muñoz Gualán, Germán G. (2020). El Sistema Educativo Militar del Ecuador: Un modelo innovador. Revista Cognosis. 5(3), Article 3. https://doi.org/10.33936/cognosis.v5i3.2448 DOI: https://doi.org/10.33936/cognosis.v5i3.2448
Muñoz, Gualán; Germán, G., Muñoz Gualán; Erik. D y Muñoz Gualán, Alberth. P. (2022). Factores que influyen en el rendimiento académico en los estudiantes de la carrera en ciencias militares. Revista Ciencias Pedagógicas e Innovación, 10(2), Article 2. https://doi.org/10.26423/rcpi.v10i2.599 DOI: https://doi.org/10.26423/rcpi.v10i2.599
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (2024). Adult Learning in the Military Context. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. https://doi.org/10.17226/27959 DOI: https://doi.org/10.17226/27959
Nicolete, Priscila Cadorin; Herpich, Fabrício; Júnior, Eduardo Tocchetto de Oliveira; Silva, Marta Adriana Machado; y Tarouco, Liane Margarida Rockenbach (2023). Análisis de estilos de aprendizaje de ingreso de un curso técnico en electromecánica con la aplicación del inventario de kolb. Tecné, Episteme y Didaxis: TED, 53(2023), 63-81. https://doi.org/10.17227/ted.num53-14128 DOI: https://doi.org/10.17227/ted.num53-14128
Peterson, Elizabeth. R..; Rayner, Stephen. G.; y Armstrong, Steven. J. (2009). Researching the psychology of cognitive style and learning style: Is there really a future? Learning and Individual Differences, 19(4), 518-523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2009.06.003 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2009.06.003
Poore, Julie A.; Cullen, Deborah L.; y Schaar, Gina L. (2014). Simulation-Based Interprofessional Education Guided by Kolb’s Experiential Learning Theory. Clinical Simulation in Nursing, 10(5), e241-e247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecns.2014.01.004 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecns.2014.01.004
Pulkka, Antti-Tuomas; y Budlong, Laura (2022). Associations Between Achievement Goal Orientations, Preferred Learning Practices, and Motivational Evaluations of Learning Environment Among Finnish Military Reservists. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 902478. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.902478 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.902478
Rodríguez Cepeda, Rodrigo (2018). Los modelos de aprendizaje de Kolb, Honey y Mumford: Implicaciones para la educación en ciencias. Sophia, 14(1), 51-64. https://www.redalyc.org/journal/4137/413755833005/html/ DOI: https://doi.org/10.18634/sophiaj.14v.1i.698
Ryder, Mike; y Downs, Carolyn (2022). Rethinking reflective practice: John Boyd’s OODA loop as an alternative to Kolb. The International Journal of Management Education, 20(3), 100703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2022.100703 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2022.100703
Sinha, Ekta (2023). ‘Co-creating’ experiential learning in the metaverse- extending the Kolb’s learning cycle and identifying potential challenges. The International Journal of Management Education, 21(3), 100875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2023.100875 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2023.100875
Wisher, R. A., y Champagne, M. V. (2000). Distance learning and training: An evaluation perspective. In S. Tobias & J. D. Fletcher (Eds.), Training & retraining: A handbook for business, industry, government, and the military (pp. 581-601). Macmillan Reference USA.
Yamazaki, Yoshitaka (2005). Learning styles and typologies of cultural differences: A theoretical and empirical comparison. International Journal of Intercultural Relations, 29(5), 521-548. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijintrel.2005.07.006 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijintrel.2005.07.006
Publicado
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2025 Danny Damian Reinoso-Ortíz (Autor); Daniela Cristina Villagómez-Capelo, Víctor Manuel Reyes (Autor)

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0.
El titular de los derechos de autor de la obra, otorga derechos de uso a los lectores mediante la licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0 Internacional. Esto permite el acceso gratuito inmediato a la obra y permite a cualquier usuario leer, descargar, copiar, distribuir, imprimir, buscar o vincular a los textos completos de los artículos, rastrearlos para su indexación, pasarlos como datos al software o usarlos para cualquier otro propósito legal.
Cuando la obra es aprobada y aceptada para su publicación, los autores conservan los derechos de autor sin restricciones, cediendo únicamente los derechos de reproducción, distribución para su explotación en formato de papel, así como en cualquier otro soporte magnético, óptico y digital.